Fertilizer Testing Methods

In order to ensure the quality and fair trade of fertilizers, specific analytical methods have been developed. These methods are used to confirm the percentage of main or guaranteed components and to measure the quantity of harmful compounds in fertilizers.
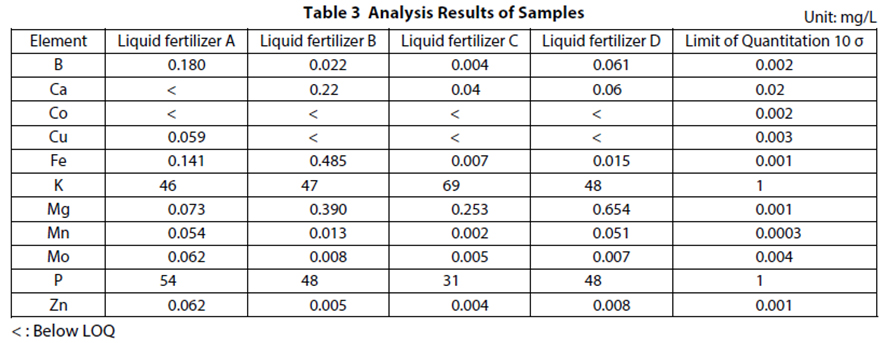
Analysis of water-soluble ingredients with ICP
In the Fertilizer Testing Method developed by the Food and Agricultural Materials Inspection Center (FAMIC), inductively-coupled plasma (ICP) atomic emission spectrometry is introduced as an analysis method for water-soluble metals. Use of the Shimadzu ICPE-9820 enables simultaneous analysis over the full range of concentrations through combined use of high sensitivity axial (AX) view and radial (RD) view observations for analysis of high concentration ingredients.
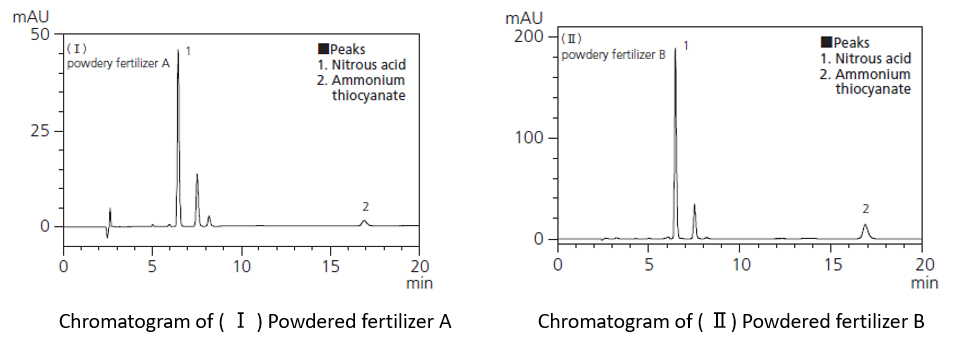
Analysis of nitrous acid and ammonium thiocyanate in fertilizers
Fertilizers with high concentrations of nitrous acid and ammonium thiocyanate have a negative effect on plant growth, so maximum content levels (permitted content levels) for these toxic substances are stipulated in official specifications for commercial fertilizers in Japanese laws. An example of the simultaneous analysis of the nitrous acid and ammonium thiocyanate content of fertilizer by HPLC is described here.
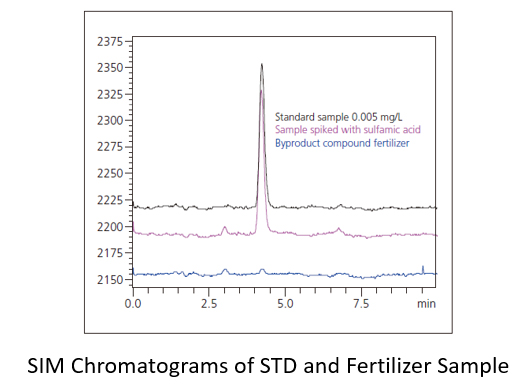
Analysis of sulfamic acid in fertilizers
Sulfamic acid, due to its plant growth inhibiting effects, is subject to maximum limits in fertilizers as specified in Japanese regulations. In the Fertilizer Testing Method developed by FAMIC, the ion chromatography (IC) method and LC/MS method are specified as the test methods for sulfamic acid in ammonium sulfate.
Here, we introduce an analytical result using LC/MS, which provides high selectivity to eliminate the effects of contaminating components.